
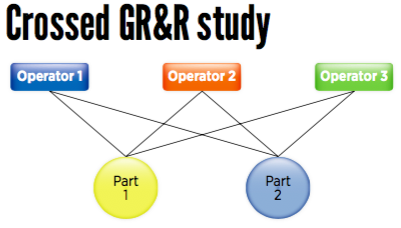
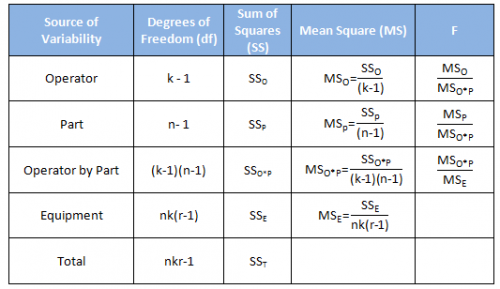
Xbar and R Charts, Interaction between Operator and Part, Comparative PlotsĨ.2.1 Creating and analyzing Full Factorial DesignsĨ.3. The Minitab dialog box Gage Linearity and Bias Study combines the analysis process into one operation to analyze gage linearity. Chiar daca organizatia Dvs are angajati incepatori in analiza datelor sau avansati in acest domeniu, sesiunea va acoperi tot ceea ce este necasar pentru a deveni un Minitab expert.Īnalisti de sistem, business analisti, belti six sigma, profesionisti in calitate, manageri de proiect, coordonatori de programe, leaderi, product manageri, executivi.ġ.4.3 Range, Variance, and Standard Deviationġ.4.4 Quiz: Using Statistics to Analyze Dataġ.4.5 Minitab Tools: Display Descriptive StatisticsĢ.2 Fundamentals of Statistical InferenceĢ.2.3 Quiz: Fundamentals of Statistical InferenceĢ.4.2 Probabilities Associated with a Normal DistributionĬhapter 3: Hypothesis Tests and Confidence Intervalsģ.2.3 Using Hypothesis Testing to Make Decisionsģ.2.4 Type I and Type II Errors and Powerģ.4.3 2 Variances Test Results 3.4.4 AssumptionsĤ.3 Control Charts for Variables Data in SubgroupsĤ.4 Control Charts for Individual Observationsĥ.4 Process Capability for Nonnormal Dataĥ.4.1 Transformations and Alternate DistributionsĦ.2 Relationship Between Two Quantitative Variablesħ.4 Graphical Analysis of a Gage R&R Studyħ.4.1 Basic Concepts (Components of Variation,
It involves repeated measurements of one part, on one. Cursurile sunt sustinute de master black belti. A Type 1 gage study is normally used to determine the baseline repeatability of a measurement system. Minitab ofera un pachet complet de instrumente pentru vizualizarea, explorarea, analiza, intelegerea datelor de business. Minitab aduce instrumentele necesare pentru analiza datelor si gasirea unor solutii la cele mai dificile probleme de business. A Cgk value of 1.33 is a common benchmark value to denote a capable gage – one that is both precise (good repeatability) and accurate (low bias).Rolul sesiunii de 3 zile de training MINITAB este de a va familiariza cu colectarea, vizualizarea si analiza datelor de business Cgk decreases as the difference between the gage's mean measurement and the reference value increases. Cgk compares the Study Variation to the tolerance, but it also considers whether the measurements are "on target". About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. Minitab also calculates the capability metric Cgk to assess repeatability and bias together. In The Menu Click Stat > Quality Tools > Gage Study > Gage R&R crossed. If a statistically significant bias exists, you conclude your gage is consistently measuring higher or lower than the correct value. Learn more about MSA Continuous Data Tests in Measure Phase, Module 3.2.1 of. Key output includes a run chart of measurements, bias statistics, and capability statistics. Essentially, this test is a 1-sample t-test to determine whether the mean measurement differs significantly from the reference value. Complete the following steps to interpret a type 1 gage study. Minitab analyzes bias with a t-test of the null hypothesis that no bias exists. In addition to repeatability, Minitab also assesses the gage's bias, which is the difference between the gage's average measurement and the official reference value – the "true" value that your gage targets. This Cg value indicates the gage's effectiveness within this tolerance range. Values of Cg greater than 1.33 indicate the spread of the gage's measurements is adequately narrow in relation to your tolerance range.įor example, with the default values of K and L, a Cg metric of 2 indicates that 20% of your tolerance range will cover the entire spread of measurements twice over. To assess a gage's repeatability, Minitab calculates the Cg metric to compare the study variation (the spread of the gage's measurements) with a percentage of the tolerance. The variation of a gage's measurements should be small compared to the tolerance. For example, if the tolerance for a cylinder's diameter is 5mm, but repeated measurements of a reference cylinder also span 5mm, you cannot trust the gage to determine whether a cylinder falls within the tolerance range. Some measurement variation will be present even in a capable gage, but if the variation is too large in relation to the part's tolerance, the gage will be too variable for its purpose. Repeatability is the gage's ability to make consistent measurements of the same part.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
